Tagus
Chronicle of an announced death?
‘Got a cold beer?’
The bartender from the restaurant Pedro dos Leitões in Mealhada looked straight into the weary eyes of a stocky man in a blue jacket with Ministry of Environment written on it
‘Sure man, here you are. Been busy?’
‘You say it. Took us ages to get decent samples.’
‘Samples? Whereof?
‘Of that paper mill nearby, in Vila Velha de Rodão. We first only got that stinking foam and had to go really deep into the river to get nice samples ’
‘Oh, you mean Celtejo?’
It had been in all the newspapers and every day on TV. Celtejo, the cellulose factory had caused a natural disaster last month by dumping enormous amounts of waste in the drought-inflicted Tagus, the country’s largest river. Thousands of fish had died and tourists fled the area. The excessive discharges had probably been going on secretly for years. The government had decided to a 50% cut in production until further notice and Francisco Ferreira from ZERO – the sustainable terrestrial system association – already claimed compensation from Celtejo of 150.000 euro for damage done. Cleaning of the mess was estimated to cost at least one million euro according to Portugal’s Minister of Environment, João Matos Fernandes.
‘Yeah, that’s the one’, nodded the client and pointed to his empty glass.
‘But why more samples?’ said the barkeeper. I thought the case was closed and Celtejo the culprit. The party for People, Animals, and Nature (PAN) demanded yesterday immediate closure of the plant. At least that’s what I’ve heard on the news.’
‘It’s not all that easy’, grumbled the official. ‘We have to be very sure before we can shut down a big company like that. Imagine what is going to happen with its 300 employees? Vila Velha completely depends on that industry. Besides that, we have to verify if its production has been really halved.
‘OK, thanks for the beer. They are expecting the data in Lisbon as of today.’
He briskly walked around the restaurant but came to an abrupt standstill when he reached the parking lot.
‘Oh no’, he whimpered when he saw the rear window of his car smashed and his PC gone.
Computer with confidential data from the Celtejo investigation stolen in restaurant Pedro dos Leitões, Mealhada
[ Expresso 23-2-2018 ]

‘The Tagus is more beautiful than the river that flows through my village,
But the Tagus is not more beautiful than the river that flows through my village
Because the Tagus is not the river that flows through my village.
The Tagus descends from Spain
And crosses Portugal to pour into the sea.
Everyone knows this.
But few know what the river in my village is called
And where it goes to
And where it comes from.
And so, because it belongs to fewer people,
The river of my village is freer and larger.’ (Fernando Pessoa, 1914)
Bom fim de semana Have a nice weekend ( photo Público)

 Both left and right wing parties in Parliament are concerned about racism in the police force and violation of human rights in prisons. The reason is a recently published report of the European Committee against Torture, stating that police violence in Portugal – in particular against African descendants – is the highest in Western Europe.
Both left and right wing parties in Parliament are concerned about racism in the police force and violation of human rights in prisons. The reason is a recently published report of the European Committee against Torture, stating that police violence in Portugal – in particular against African descendants – is the highest in Western Europe. The committee – that also visited the country in 2013 – emphasizes that the police violence at police stations has increased and that the situation in the overcrowded prisons of Caxias, Setubal, and Lisbon is ‘inhuman and degrading.’
The committee – that also visited the country in 2013 – emphasizes that the police violence at police stations has increased and that the situation in the overcrowded prisons of Caxias, Setubal, and Lisbon is ‘inhuman and degrading.’ Julia Kozma, lawyer and chairing the European delegation, points the finger towards the Ministry of Internal Affairs – responsible for the police and the security forces – and regrets its lack of ‘awareness’. The Ministry denies the accusations and declares that ‘all complaints about violent police conduct are investigated by the Internal General Inspectorate (IGAI) and immediately reported to the Public Prosecutor.’
Julia Kozma, lawyer and chairing the European delegation, points the finger towards the Ministry of Internal Affairs – responsible for the police and the security forces – and regrets its lack of ‘awareness’. The Ministry denies the accusations and declares that ‘all complaints about violent police conduct are investigated by the Internal General Inspectorate (IGAI) and immediately reported to the Public Prosecutor.’ The reality, however, is that only a very small number of the complaints are brought before court. ‘And that’s exactly the problem’, says Kozma. ‘There is a spirit of impunity and bureaucracy, whereby complaining doesn’t help. The inspection body (IGAI) needs more skills to conduct criminal investigations and more resources to act independently.’
The reality, however, is that only a very small number of the complaints are brought before court. ‘And that’s exactly the problem’, says Kozma. ‘There is a spirit of impunity and bureaucracy, whereby complaining doesn’t help. The inspection body (IGAI) needs more skills to conduct criminal investigations and more resources to act independently.’ In recent months the non-governmental organization SOS racism received an increasing number of grievances from inmates in the prison of Lisbon about racist provocations and intimidations. Peculiar was that all complaints came from African immigrants and that any registration on xenophobe or racist behavior from the guards and staff is lacking.
In recent months the non-governmental organization SOS racism received an increasing number of grievances from inmates in the prison of Lisbon about racist provocations and intimidations. Peculiar was that all complaints came from African immigrants and that any registration on xenophobe or racist behavior from the guards and staff is lacking. Patients have to wait 3 years to see a urologist in Vila Real or an ENT specialist in Leiria and 2 years to obtain an appointment with a cardiologist in Guarda. These extremes not only occur in the countryside, as the waiting list for a neurological consultation at Amadora Sintra – one of the biggest state hospitals in the country – exceeds more than a year.
Patients have to wait 3 years to see a urologist in Vila Real or an ENT specialist in Leiria and 2 years to obtain an appointment with a cardiologist in Guarda. These extremes not only occur in the countryside, as the waiting list for a neurological consultation at Amadora Sintra – one of the biggest state hospitals in the country – exceeds more than a year. The average waiting period for (non-acute) specialist care in Portugal is 4 months, varying from 6 months for an ophthalmologist to 6 weeks for an obstetrician. Patients who have to wait for more than five months have – by law – the right to be treated in the private sector. A costly buffer as the SNS, respectively the taxpayer must pay the bill.
The average waiting period for (non-acute) specialist care in Portugal is 4 months, varying from 6 months for an ophthalmologist to 6 weeks for an obstetrician. Patients who have to wait for more than five months have – by law – the right to be treated in the private sector. A costly buffer as the SNS, respectively the taxpayer must pay the bill. The excessive waiting lists are – according to the independent trade union of doctors Sindicato Independente dos Médicos – mainly the result of the fact that specialists in state hospitals have to spend too much – almost half – of their time to emergencies. The majority of the specialists working in the SNS is therefore unsatisfied. Many want to abandon the service and either go into private practice or leave the country, where working conditions are better and the pay higher.
The excessive waiting lists are – according to the independent trade union of doctors Sindicato Independente dos Médicos – mainly the result of the fact that specialists in state hospitals have to spend too much – almost half – of their time to emergencies. The majority of the specialists working in the SNS is therefore unsatisfied. Many want to abandon the service and either go into private practice or leave the country, where working conditions are better and the pay higher. ‘Wages are indeed low, excess hours abundant and career prospects nil’, explains Maria Ferreira of the Public Health Department of the University of Porto, who conducted an investigation under 15.000 doctors in northern Portugal. ‘Half of the recently qualified doctors is thinking of leaving the country after finishing their specialization and over 1200 doctors have already left in the past 3 years.’
‘Wages are indeed low, excess hours abundant and career prospects nil’, explains Maria Ferreira of the Public Health Department of the University of Porto, who conducted an investigation under 15.000 doctors in northern Portugal. ‘Half of the recently qualified doctors is thinking of leaving the country after finishing their specialization and over 1200 doctors have already left in the past 3 years.’ A draft legislation thereupon was submitted in July 2017 and discussed in Parliament early this year. Heloísa Apolónia – MP of the Ecological and Green Party (PEV) – explains ‘our proposal is to ban the use of plastic disposables in restaurants and bars and to look for biodegradable substitutes within 3 years.’
A draft legislation thereupon was submitted in July 2017 and discussed in Parliament early this year. Heloísa Apolónia – MP of the Ecological and Green Party (PEV) – explains ‘our proposal is to ban the use of plastic disposables in restaurants and bars and to look for biodegradable substitutes within 3 years.’ António Fonseca, the president of the Association of Bars in the Historic Center of Porto (ABZHP) – that encourages the legalization of the use of alcohol in public places – believes that the plans are irresponsible in the light of the danger glassware can cause in nightlife.
António Fonseca, the president of the Association of Bars in the Historic Center of Porto (ABZHP) – that encourages the legalization of the use of alcohol in public places – believes that the plans are irresponsible in the light of the danger glassware can cause in nightlife.

 ‘This earthquake can be considered as moderately severe’, says Fernando Carrilho, chief seismologist at the IPMA (Portuguese Institute of the Sea and Atmosphere). ‘People shouldn’t worry too much as the southern part of the country has always been seismic active.’
‘This earthquake can be considered as moderately severe’, says Fernando Carrilho, chief seismologist at the IPMA (Portuguese Institute of the Sea and Atmosphere). ‘People shouldn’t worry too much as the southern part of the country has always been seismic active.’ ‘Preventive measures are warranted’, especially in the densely populated areas in the south – like Lisbon and the Algarve – that are most at risk’, says Daniel Oliveira, a civil engineer at the University of Minho. ‘Although a law from 1958 requires earthquake-proof construction, most buildings in the historic capital date from before that time and there is hardly any monitoring of the implementation of the law.’
‘Preventive measures are warranted’, especially in the densely populated areas in the south – like Lisbon and the Algarve – that are most at risk’, says Daniel Oliveira, a civil engineer at the University of Minho. ‘Although a law from 1958 requires earthquake-proof construction, most buildings in the historic capital date from before that time and there is hardly any monitoring of the implementation of the law.’ Over the past 500 years, Portugal has suffered four major earthquakes – in 1531, 1755, 1909 and 1969 – with a magnitude of 6 or more on the Richter scale. The biggest and by far most tragic one was in 1755. With a magnitude of 9 on the Richter scale, it developed apocalyptic proportions and completely wiped out the lower part of the capital. This earthquake (terramoto) inspired poets, influenced philosophers, activated prophets and motivated politicians – like the Marquis of Pombal – to a completely new architectural reconstruction of the Baixa, Lisbon’s city center.
Over the past 500 years, Portugal has suffered four major earthquakes – in 1531, 1755, 1909 and 1969 – with a magnitude of 6 or more on the Richter scale. The biggest and by far most tragic one was in 1755. With a magnitude of 9 on the Richter scale, it developed apocalyptic proportions and completely wiped out the lower part of the capital. This earthquake (terramoto) inspired poets, influenced philosophers, activated prophets and motivated politicians – like the Marquis of Pombal – to a completely new architectural reconstruction of the Baixa, Lisbon’s city center.

 Nowadays, half of the children are born outside marriage and in 20% parents also do not live together, a number that has doubled in the last 6 years.
Nowadays, half of the children are born outside marriage and in 20% parents also do not live together, a number that has doubled in the last 6 years. In parallel to a decline in the number of marriages, there has been an increase in the number of divorces, with Portugal ranking first in Europe. Remarkable is that women have to wait longer than men before they can remarry, ten months instead of six!
In parallel to a decline in the number of marriages, there has been an increase in the number of divorces, with Portugal ranking first in Europe. Remarkable is that women have to wait longer than men before they can remarry, ten months instead of six! Same-sex marriages comprise only 1% of the wedlock but are four times more common in Lisbon and Porto than in the sparsely populated interior. Since 2010 – when gay marriage became legally possible in Portugal – 2300 gay couples have married, two-thirds being men.
Same-sex marriages comprise only 1% of the wedlock but are four times more common in Lisbon and Porto than in the sparsely populated interior. Since 2010 – when gay marriage became legally possible in Portugal – 2300 gay couples have married, two-thirds being men. Portugal’s famous pavement originates from the nineteenth century.
Portugal’s famous pavement originates from the nineteenth century.  Calçada Portuguesa ( Portuguese-style pavement) is characterized by tight paving with small, irregularly shaped – usually white and black – limestones. Not only ships, animals, stars, flowers, anchors or mermaids inhabit the ground, also geometric patterns show themselves as magnificent stony carpets. Their extraordinary symmetry is impressive in this respect.
Calçada Portuguesa ( Portuguese-style pavement) is characterized by tight paving with small, irregularly shaped – usually white and black – limestones. Not only ships, animals, stars, flowers, anchors or mermaids inhabit the ground, also geometric patterns show themselves as magnificent stony carpets. Their extraordinary symmetry is impressive in this respect. Figures in artistic sidewalks and squares – characterized by the application of stones of different color and shape – were traditionally performed with the aid of wooden molds. The base-color stone, usually white, is first laid around the mold and after removal, the darker stones are fitted inside.
Figures in artistic sidewalks and squares – characterized by the application of stones of different color and shape – were traditionally performed with the aid of wooden molds. The base-color stone, usually white, is first laid around the mold and after removal, the darker stones are fitted inside. Advantages of mosaic pavement are the use of local materials, its sustainability (stones can be re-used), the ease of removal, the invisibility of restorations (when performed professionally), the efficient drainage and its cultural and touristic value.
Advantages of mosaic pavement are the use of local materials, its sustainability (stones can be re-used), the ease of removal, the invisibility of restorations (when performed professionally), the efficient drainage and its cultural and touristic value.

 Since Portugal has been declared World’s Leading Destination and Lisbon Best City Break in 2017, I’ am sure you are dying to visit the country in order to see for yourself, whether these prestigious awards are justified.
Since Portugal has been declared World’s Leading Destination and Lisbon Best City Break in 2017, I’ am sure you are dying to visit the country in order to see for yourself, whether these prestigious awards are justified.  However, that hasn’t always been the case. It started as a forced task performed by prisoners in the nineteenth century. Only later it evolved into a craft and pavers (calceteiros) became recognized artisans, whose art became appreciated in such a way, that it spread to many cities and continents.
However, that hasn’t always been the case. It started as a forced task performed by prisoners in the nineteenth century. Only later it evolved into a craft and pavers (calceteiros) became recognized artisans, whose art became appreciated in such a way, that it spread to many cities and continents. It became an immediate success and similar works were ordered, such as the paving of Lisbon’s major square Praça D. Pedro IV – popularly known as Rossio (meaning ‘wide and public space’) – that took place between 1846 and 1849.
It became an immediate success and similar works were ordered, such as the paving of Lisbon’s major square Praça D. Pedro IV – popularly known as Rossio (meaning ‘wide and public space’) – that took place between 1846 and 1849. The pavement of Rossio was called ‘Wide Sea’ (Mar Largo) for depicting waves, symbolizing the encounter between the Tagus river and the Atlantic Ocean, which launched the Portuguese into the Discoveries in the 15th century. After Rossio, Lisbon adopted mosaic pavement for all its squares and sidewalks and it became the most popular pavement in historic Portuguese towns and famous worldwide.
The pavement of Rossio was called ‘Wide Sea’ (Mar Largo) for depicting waves, symbolizing the encounter between the Tagus river and the Atlantic Ocean, which launched the Portuguese into the Discoveries in the 15th century. After Rossio, Lisbon adopted mosaic pavement for all its squares and sidewalks and it became the most popular pavement in historic Portuguese towns and famous worldwide.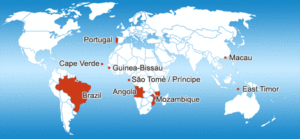 The majority of the ‘new citizens’ originate from Portuguese speaking countries such as Brazil (120.000), Cape Verde (75.000), Guinea–Bissau (35.000), and Angola (35.000). During the same period, a considerable number of Ukrainians (25.000) and Romanians (30.000) settled in the country.
The majority of the ‘new citizens’ originate from Portuguese speaking countries such as Brazil (120.000), Cape Verde (75.000), Guinea–Bissau (35.000), and Angola (35.000). During the same period, a considerable number of Ukrainians (25.000) and Romanians (30.000) settled in the country.
 Timothy Macedo – from the NGO Solidaridade Imigrante (SOLEM) – is happy with the new law, but points out that there are more than 30.000 illegals (the vast majority living in Lisbon) and that most of them are waiting for years to be assessed by the Foreigners and Borders Service (SEF).
Timothy Macedo – from the NGO Solidaridade Imigrante (SOLEM) – is happy with the new law, but points out that there are more than 30.000 illegals (the vast majority living in Lisbon) and that most of them are waiting for years to be assessed by the Foreigners and Borders Service (SEF). It all started in July 2016 when the national football team – with captain Cristiano Ronaldo as the best male footballer in the world – won the European Football Championship for the first time in history.
It all started in July 2016 when the national football team – with captain Cristiano Ronaldo as the best male footballer in the world – won the European Football Championship for the first time in history.
 Nine months after the Football Championship, Portugal delivered another number one, by winning the Eurovision Song Contest 2017 with Salvador Sobral’s ‘Amar Pelos Dois’ [
Nine months after the Football Championship, Portugal delivered another number one, by winning the Eurovision Song Contest 2017 with Salvador Sobral’s ‘Amar Pelos Dois’ [ Seven months after the Eurovision Song contest the Portuguese economist and Minister of Finance – Mário Centeno – was elected as the next president of the Eurogroup, an informal but powerful gathering of 19 eurozone finance ministers. Centeno will be the first holder of the post from one of the South-European countries forced into a bailout by the euro crisis.
Seven months after the Eurovision Song contest the Portuguese economist and Minister of Finance – Mário Centeno – was elected as the next president of the Eurogroup, an informal but powerful gathering of 19 eurozone finance ministers. Centeno will be the first holder of the post from one of the South-European countries forced into a bailout by the euro crisis. And last but not least, just before the end of this year, the World Travel Awards designated Portugal as the World’s Leading Destination in tourism. It is the first time that a European country wins this prestigious award. In addition, Lisbon won the award for best City Break in the world. The WTA’s – founded in 1993 – are internationally considered as ‘the Oscar’s of tourism’. In September Portugal had already won the award for Europe’s Leading Destination [
And last but not least, just before the end of this year, the World Travel Awards designated Portugal as the World’s Leading Destination in tourism. It is the first time that a European country wins this prestigious award. In addition, Lisbon won the award for best City Break in the world. The WTA’s – founded in 1993 – are internationally considered as ‘the Oscar’s of tourism’. In September Portugal had already won the award for Europe’s Leading Destination [