Centre-right wins election as far-right makes record gains

Portugal’s centre-right Democratic Alliance (AD) has won the country’s third parliamentary election in three years as the underperforming socialists were left for second place, together with the far-right party Chega (meaning ‘Enough’).

Luís Montenegro, the leader of the AD – that has governed the country since its narrow victory last year – won 32.7% of the vote, taking 89 seats in the country’s 230-seat parliament, leaving it far of the 116 needed for a majority.
The Socialist Party (PS) took 23.4% of the vote to Chega’s 22.6%, tiding the two on 58 seats each.

Votes from abroad, which are to be counted in the coming days, can still put Chega ahead of the Socialist party, which would be the first time in almost forty years that the Socialists do not finish in the top two. In the last election, held 14 months ago, the AD won 80 seats, PS 78 and Chega – led by the former TV football pundit André Ventura – increased its seat count from 12 to 50 in Parliament.

For now, Chega’s delight will be tempered by Montenegro’s explicit refusal to strike any deals with Ventura’s party. ‘Governing with Chega is impossible for three reasons’, the prime minister previously stated. ‘It isn’t reliable in its thinking; it behaves like a political weathervane, always changing its mind, and it’s not suited to the exercise of government.’

The early election was triggered in March after Prime Minister Montenegro used a confidence vote in his minority government to try to head off growing scrutiny questions over his family business activities he founded in 2021 and which he transferred to his wife and sons the following year. But as he failed to win the confidence in Parliament a new election became inevitable.
In the international press terms such as ‘triumph of the conservatives ‘and ‘conservative legislature’ are used to underline the outcome of the ballots.

The British newspaper The Guardian emphasizes the record results of the right and puts into context the emergence of the Chega party, which has grown the most in terms of the number of MP’s. In Spain, El Pais refers to the ‘revolution that took place’ in Portugal which ended with the resignation of the leader of the Socialist Party Pedro Nuno Santos.

The French paper Le Monde also mentions the ‘major defeat’ of the Socialist Party and the ‘explosive growth’ of Chega. The paper highlights above all ‘the tightening of the migration policy, previously one of the most flexible in Europe under António’s Costa Socialist government. According to Italy’s La Republica, ‘the ultra-right flies, socialists fall’ and Brazil’s Folha de São Paulo reports the re-election of the Prime Minister and ‘sees ultra-right equal socialist seats in left-wing collapse.’
Enjoy the week Approveite a semana (pic Público/Sapo)





















 The history of Lisbon and Mouraria – one of the city’s oldest quarters – both originate from the presence of diverse people and cultures. In 1143, Lisbon was conquered from the Moors by King Alfonso Henriques, becoming a Christian city. The birth of Mouraria goes back to the same period, built outside the walls as the only territory where Moors were authorized to reside.
The history of Lisbon and Mouraria – one of the city’s oldest quarters – both originate from the presence of diverse people and cultures. In 1143, Lisbon was conquered from the Moors by King Alfonso Henriques, becoming a Christian city. The birth of Mouraria goes back to the same period, built outside the walls as the only territory where Moors were authorized to reside. In the 16th century, the first black migrants were forced into slavery in Lisbon, in that era the largest European centre of the flourishing slave trade. The number of slaves present in the capital reached 10% of the total population, that time comprising 100,000 inhabitants.
In the 16th century, the first black migrants were forced into slavery in Lisbon, in that era the largest European centre of the flourishing slave trade. The number of slaves present in the capital reached 10% of the total population, that time comprising 100,000 inhabitants.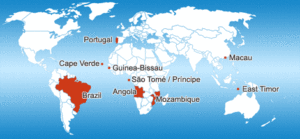 On 25 April 1974, Portugal became a democracy after 48 years of dictatorship. Between April and November 1975, Portugal took in half a million Portuguese and their descendants from its
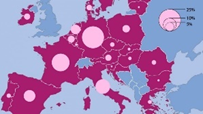
On 25 April 1974, Portugal became a democracy after 48 years of dictatorship. Between April and November 1975, Portugal took in half a million Portuguese and their descendants from its  Mouraria is the most multicultural neighbourhood of the capital. Here you find everything from African grocers to Chines tea, Indian clothing, religious talismans, Bengali restaurants, mosques and halal butchers. The percentage of foreign residents (25%) is well above the average for the city (10%) and the nation (less 4%).
Mouraria is the most multicultural neighbourhood of the capital. Here you find everything from African grocers to Chines tea, Indian clothing, religious talismans, Bengali restaurants, mosques and halal butchers. The percentage of foreign residents (25%) is well above the average for the city (10%) and the nation (less 4%). In the heart of Mouraria resides the
In the heart of Mouraria resides the 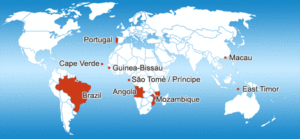 The majority of the ‘new citizens’ originate from Portuguese speaking countries such as Brazil (120.000), Cape Verde (75.000), Guinea–Bissau (35.000), and Angola (35.000). During the same period, a considerable number of Ukrainians (25.000) and Romanians (30.000) settled in the country.
The majority of the ‘new citizens’ originate from Portuguese speaking countries such as Brazil (120.000), Cape Verde (75.000), Guinea–Bissau (35.000), and Angola (35.000). During the same period, a considerable number of Ukrainians (25.000) and Romanians (30.000) settled in the country.
 Timothy Macedo – from the NGO Solidaridade Imigrante (SOLEM) – is happy with the new law, but points out that there are more than 30.000 illegals (the vast majority living in Lisbon) and that most of them are waiting for years to be assessed by the Foreigners and Borders Service (SEF).
Timothy Macedo – from the NGO Solidaridade Imigrante (SOLEM) – is happy with the new law, but points out that there are more than 30.000 illegals (the vast majority living in Lisbon) and that most of them are waiting for years to be assessed by the Foreigners and Borders Service (SEF).