Amidst the height of the country’s fight against Covid-19, the Democratic Union of Nurses in Portugal Sindepor went on a five-day ‘wake-up call’ strike last week, during which only minimum services were provided.
Carlos Ramalho, the president of the syndicate, declared that the walkout was necessary as the nurses are exhausted and their situation in the SNS (National Health Service) deteriorating.

‘We are talking about a process of many years in which the problems have not been resolved by the Government. At this point, the work overload is such that nurses can’t take anymore’.
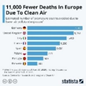
The union leader further stresses that Portugal is one of the OECD countries with the least number of nurses per 1,000 inhabitants.

At the same time, the Ordem dos Enfermeiros (Order of Nurses) expressed concern about the recruitment of Portuguese nurses in Europe, revealing that hunting for nurses has intensified from countries such as Spain, the UK and the Netherlands.
These countries are offering lucrative annual contracts for hospitals and nursing homes. From Spain, there have been contracts with offers of 30,000 euros per year, almost double the salary in Portugal. The Netherlands on the other hand is providing – in addition to an ample salary – accommodation, transport and travel.
The OE recalls that ‘although the recognition of the nurses is unanimous, there is no incentive nor decent pay’. Last year more than 4,000 nurses asked the order for a declaration for emigration purposes, a record number that tripled compared to 2017 and represents an increase of 68% compared to 2018.

‘Given the severe situation we are going through – after nine months into the pandemic – it is imperative that the way nurses are hired as well as their working conditions must be improved. There are almost 20,000 nurses abroad and the Government should be concerned with creating means for them to return’, declared OE’s chairwoman Ana Rita Cavaco.
‘We just can’t afford to export more nurses’.
Keep fit Fique saudável (pic Público/Sapo)