The Chinese leaf that conquered the world
 There are roughly two ways to say tea in the world. One is like the English expression – thee in Dutch, tee in German or thé in French. The other is a variation of cha – chay in Russian, chai in Swahili or shay in Arabic. Both variations come from China. The words that sound like cha spread across the land, the tea saying spread over water.
There are roughly two ways to say tea in the world. One is like the English expression – thee in Dutch, tee in German or thé in French. The other is a variation of cha – chay in Russian, chai in Swahili or shay in Arabic. Both variations come from China. The words that sound like cha spread across the land, the tea saying spread over water.
The term cha – Chinese for tea – originates from central China and made its way through Asia – along the Silk Road over 2000 years ago – becoming chay in Hindi and Persian.
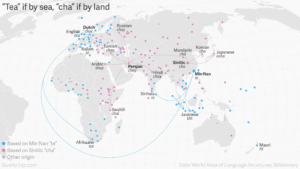 But the Chinese character for cha is pronounced as te in the Min Nan variety of Chinese, spoken in the coastal province of Fujian.
But the Chinese character for cha is pronounced as te in the Min Nan variety of Chinese, spoken in the coastal province of Fujian.
This te form spread to Europe via the Dutch East Indian Company, who became the primary traders of tea between Europe and China in the 17th century.
Yet the Dutch were not the first in Asia. That privilege belonged to the Portuguese, who didn’t trade through Fujian but Macao, where cha is used. That’s why of all Western European countries only Portugal uses the cha word for tea!
 Although it’s fairly commonly known that tea originated in China, it is far less known that it was a particular Portuguese woman, who inspired its popularity in England. Let’s go back to 1662, when Catherine of Braganza – daughter of Portugal’s King John IV – married England’s King Charles II, and became the Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland. Travelling up north to join her husband, she is said to have taken along loose-leaf tea, that was popular among Portugal’s aristocracy.
Although it’s fairly commonly known that tea originated in China, it is far less known that it was a particular Portuguese woman, who inspired its popularity in England. Let’s go back to 1662, when Catherine of Braganza – daughter of Portugal’s King John IV – married England’s King Charles II, and became the Queen of England, Scotland, and Ireland. Travelling up north to join her husband, she is said to have taken along loose-leaf tea, that was popular among Portugal’s aristocracy.
When Catherine arrived in England, tea was being consumed there only as herbal medicine and very expensive. The reason for the cost was that England had no direct trade with China and the small quantities the Dutch were importing were so pricey, that only the wealthiest could afford it. Tea became associated with the elite women’s society around the royal court, of which Catherine was the famous centrepiece.
‘The best of Queens, and the best of herbs, we owe
To that bold nation, which the way did show
To the fair region where the sun doth rise,
Whose rich productions we so justly prize.’
( Birthday ode to Queen Catherine. Edmund Waller, 1663 )
Aproveite sua semana Enjoy your week (pic 2 qz.com)

 In the heart of Lisbon – on the Santana hill between the Travessa da Pena and the Beco de São Luis – used to be the clothing manufactory of Ramiro Leão.
In the heart of Lisbon – on the Santana hill between the Travessa da Pena and the Beco de São Luis – used to be the clothing manufactory of Ramiro Leão. Ramiro Leão (1857-1934), born in Gavião moved young to the capital, where he became one of the most powerful merchants and founder of the cosmopolitan warehouse Ramiro Leão & Co (nowadays United Colors of Benneton) in the glamorous Chiado neighbourhood.
Ramiro Leão (1857-1934), born in Gavião moved young to the capital, where he became one of the most powerful merchants and founder of the cosmopolitan warehouse Ramiro Leão & Co (nowadays United Colors of Benneton) in the glamorous Chiado neighbourhood. Since the old factory broke down, it experienced a complete facelift and is nowadays a graceful blue eye-catcher in the skyline of Lisbon with nine apartments, a lush Mediterranean garden and a magnificent city view.
Since the old factory broke down, it experienced a complete facelift and is nowadays a graceful blue eye-catcher in the skyline of Lisbon with nine apartments, a lush Mediterranean garden and a magnificent city view. In protest against this dismissal, a massive strike takes place the next day outside the gates of the factory. The strikers look for Ramiro Leão but he refuses to recognize the Union and its members. The peaceful protest lasts about four and a half hours and is finally swept away by military force.
In protest against this dismissal, a massive strike takes place the next day outside the gates of the factory. The strikers look for Ramiro Leão but he refuses to recognize the Union and its members. The peaceful protest lasts about four and a half hours and is finally swept away by military force. It all began hundreds of years ago (
It all began hundreds of years ago ( King Manuel, who was not pleased with this prerequisite, came up with an alternative, that Jews would be allowed to stay if they converted to Christianity. Some did and became New Christians (Conversos), others
King Manuel, who was not pleased with this prerequisite, came up with an alternative, that Jews would be allowed to stay if they converted to Christianity. Some did and became New Christians (Conversos), others  But how did fish and chips ended up being served together? There are many claims about who created the pairing. Most trace it back to the early 1860s when Joseph Malins, a Jewish immigrant, opened up a fish and chips shop in London. Other theories point to John Lee, a man from Mossley, near Manchester, who ran in 1863 a ‘chipped potato’ restaurant that sold the popular combination.
But how did fish and chips ended up being served together? There are many claims about who created the pairing. Most trace it back to the early 1860s when Joseph Malins, a Jewish immigrant, opened up a fish and chips shop in London. Other theories point to John Lee, a man from Mossley, near Manchester, who ran in 1863 a ‘chipped potato’ restaurant that sold the popular combination.
 In its back the former Medical-Surgical School – now the Faculty of Medical Sciences of the New University of Lisbon – at its feet an immense heap of marble plates engraved with thanks for graces and miracles performed. Remarkable is the complete absence of religious symbols on these ex-votes. Was the figure in bronze on the pedestal a prestigious doctor, a saint or both?
In its back the former Medical-Surgical School – now the Faculty of Medical Sciences of the New University of Lisbon – at its feet an immense heap of marble plates engraved with thanks for graces and miracles performed. Remarkable is the complete absence of religious symbols on these ex-votes. Was the figure in bronze on the pedestal a prestigious doctor, a saint or both? Dr Sousa Martins (1843-1897) gave special relevance to the doctor-patient relationship, teaching his students at the Hospital São José (St Joseph’s hospital) not only to treat but most of all to cherish the patients. One of his lessons was that if a doctor had nothing to relieve the suffering of the patient, he would still have a smile. Although famous as a pioneer in teaching, a brilliant scientist and doctor of the Royal Family, he never liked being credited with such notoriety and affirmed himself as ‘progressive and Freemason’.
Dr Sousa Martins (1843-1897) gave special relevance to the doctor-patient relationship, teaching his students at the Hospital São José (St Joseph’s hospital) not only to treat but most of all to cherish the patients. One of his lessons was that if a doctor had nothing to relieve the suffering of the patient, he would still have a smile. Although famous as a pioneer in teaching, a brilliant scientist and doctor of the Royal Family, he never liked being credited with such notoriety and affirmed himself as ‘progressive and Freemason’. Sousa Martins gained enormous prestige in his fight against tuberculosis – which at that time reached epidemic proportions in Lisbon – and his name will forever be linked to Portugal’s first sanatorium in the Serra da Estrella, a mountainous region in the centre of the country.
Sousa Martins gained enormous prestige in his fight against tuberculosis – which at that time reached epidemic proportions in Lisbon – and his name will forever be linked to Portugal’s first sanatorium in the Serra da Estrella, a mountainous region in the centre of the country. As a dedicated physician, he always was in direct contacts with his patients. The – at that time incurable – infectious disease he fought so hard during his medical career, coupled with a heart injury, eventually killed him.
As a dedicated physician, he always was in direct contacts with his patients. The – at that time incurable – infectious disease he fought so hard during his medical career, coupled with a heart injury, eventually killed him. Portugal prepares to vote in Sunday’s general election.
Portugal prepares to vote in Sunday’s general election. For the ruling Socialist party (PS) climate change adaptation is also needed. But that isn’t enough. The party defines concrete targets for 2030 and others for 2050, such as carbon neutrality. The PS wishes to reinforce the capacity of wind farms and – faced with extreme weather – extend forecasting and warning systems. Empowering farmers ‘to adopt good practices’ is also called for.
For the ruling Socialist party (PS) climate change adaptation is also needed. But that isn’t enough. The party defines concrete targets for 2030 and others for 2050, such as carbon neutrality. The PS wishes to reinforce the capacity of wind farms and – faced with extreme weather – extend forecasting and warning systems. Empowering farmers ‘to adopt good practices’ is also called for.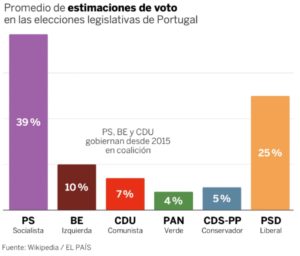 The Left Bloc (BE) is in favour of a Climate Law, an Energy Base Law and a Ministry of Climate Action. The far-left party advocates the end of fossil fuel car production by 2025 and coal-fired power generation by 2023, in the meantime accelerating solar production. It also intends to ban cars from city centres and strives for free public transport, favouring investment in ‘rail mode’.
The Left Bloc (BE) is in favour of a Climate Law, an Energy Base Law and a Ministry of Climate Action. The far-left party advocates the end of fossil fuel car production by 2025 and coal-fired power generation by 2023, in the meantime accelerating solar production. It also intends to ban cars from city centres and strives for free public transport, favouring investment in ‘rail mode’. The millennium Animal and Nature party (PAN) – founded in 2009 – wants vegetarian meals at state-sponsored events, prevention of any exploitation of hydrocarbons and the closure of all coal plants by 2023. Furthermore financial benefits for cycling to work, measures to reduce car traffic, restrictions on night air traffic and the suspension of the construction of a new airport.
The millennium Animal and Nature party (PAN) – founded in 2009 – wants vegetarian meals at state-sponsored events, prevention of any exploitation of hydrocarbons and the closure of all coal plants by 2023. Furthermore financial benefits for cycling to work, measures to reduce car traffic, restrictions on night air traffic and the suspension of the construction of a new airport. However, the level of commitment of all six major parties is far too low, argues a group of independent citizens,
However, the level of commitment of all six major parties is far too low, argues a group of independent citizens,  The polls suggest António Costa’s Socialist party will win but fall short of an absolute majority in parliament.
The polls suggest António Costa’s Socialist party will win but fall short of an absolute majority in parliament. Prepared in azeite (olive oil) or tomato sauce, canned fish – the country’s original fast food – is not only cheap but also rich in omega-3, protein and calcium.
Prepared in azeite (olive oil) or tomato sauce, canned fish – the country’s original fast food – is not only cheap but also rich in omega-3, protein and calcium.  Tinned fish has been part of Portugal’s culinary heritage since 1853 when the national canning industry was born. The traditional production process of selecting, cleaning and cooking the fish to individually canning and wrapping the tins – in 90% still done by hand – hasn’t changed much over time. Sardines are processed and canned the day they are caught and age in the can for maximum flavour.
Tinned fish has been part of Portugal’s culinary heritage since 1853 when the national canning industry was born. The traditional production process of selecting, cleaning and cooking the fish to individually canning and wrapping the tins – in 90% still done by hand – hasn’t changed much over time. Sardines are processed and canned the day they are caught and age in the can for maximum flavour.


 None other than the ANICP – Portuguese National Association of Canned Fish Manufactures – is behind the
None other than the ANICP – Portuguese National Association of Canned Fish Manufactures – is behind the  Every major city in Europe is warmer in the 21st century than it was in the 20th. In December 2015, 195 member states of the UN agreed in the Paris Agreement to limit the temperature increase to 1.5⁰C above preindustrial levels. For several cities on the Iberian Peninsula, this 1.5⁰C threshold has already been reached.
Every major city in Europe is warmer in the 21st century than it was in the 20th. In December 2015, 195 member states of the UN agreed in the Paris Agreement to limit the temperature increase to 1.5⁰C above preindustrial levels. For several cities on the Iberian Peninsula, this 1.5⁰C threshold has already been reached. Even limited temperature increases have severe consequences. A hotter atmosphere can absorb more water leading to severe floods between longer and dryer periods. Heatwaves lead to excess mortality and mosquito-borne diseases like dengue fever has been creeping North with epidemics in Portugal in 2012. Recent research shows that when the daily temperature increases above 22⁰C,
Even limited temperature increases have severe consequences. A hotter atmosphere can absorb more water leading to severe floods between longer and dryer periods. Heatwaves lead to excess mortality and mosquito-borne diseases like dengue fever has been creeping North with epidemics in Portugal in 2012. Recent research shows that when the daily temperature increases above 22⁰C, 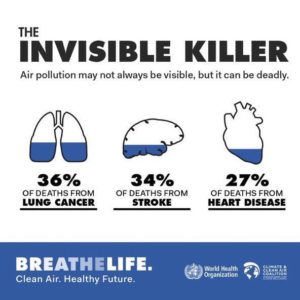 Although Portugal had in 2018 the highest
Although Portugal had in 2018 the highest 
 Massive amounts of particulate matter and sulphur dioxide (SO2) have made Lisbon’s port the sixth most polluting in Europe.
Massive amounts of particulate matter and sulphur dioxide (SO2) have made Lisbon’s port the sixth most polluting in Europe. In order to prevent global warming
In order to prevent global warming  In 2001 Portugal became – under the leadership of prime minister António Guterres, nowadays UN’s Secretary-General – the first country to ‘
In 2001 Portugal became – under the leadership of prime minister António Guterres, nowadays UN’s Secretary-General – the first country to ‘ Despite predictions at the time of an increase in drug use and drug tourism by opponents of decriminalization, the opposite happened with huge drops in drug use, overdose deaths, drug-related crime, and HIV infection. New cases of
Despite predictions at the time of an increase in drug use and drug tourism by opponents of decriminalization, the opposite happened with huge drops in drug use, overdose deaths, drug-related crime, and HIV infection. New cases of  The country’s
The country’s  What did and what did the country not do?
What did and what did the country not do? There are currently two Threshold Mobile Units in Lisbon – attending approximately 1,200 people a day – and 170 recovery facilities in a country of 10 million people for treatment and education about the harmful effects of drugs.
There are currently two Threshold Mobile Units in Lisbon – attending approximately 1,200 people a day – and 170 recovery facilities in a country of 10 million people for treatment and education about the harmful effects of drugs. While other states have developed various forms of de facto decriminalization – whereby substances perceived to be less harmful (such as cannabis) rarely lead to criminal prosecution – Portugal remains the only EU member state with a law explicitly declaring drugs to be ‘decriminalized.’
While other states have developed various forms of de facto decriminalization – whereby substances perceived to be less harmful (such as cannabis) rarely lead to criminal prosecution – Portugal remains the only EU member state with a law explicitly declaring drugs to be ‘decriminalized.’
 What does this mean for the health of the Portuguese? Excessive alcohol intake is associated with road traffic accidents, cancer, diabetes, heart disease, domestic violence, and suicide attempts.
What does this mean for the health of the Portuguese? Excessive alcohol intake is associated with road traffic accidents, cancer, diabetes, heart disease, domestic violence, and suicide attempts.
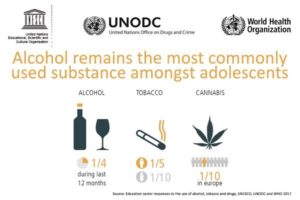
 Given the fact that there is no
Given the fact that there is no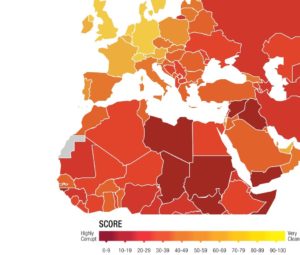 Perceived corruption in Portugal has for many years been just below the
Perceived corruption in Portugal has for many years been just below the  The low number of convictions and the fact that
The low number of convictions and the fact that  Corruption costs the country at least
Corruption costs the country at least 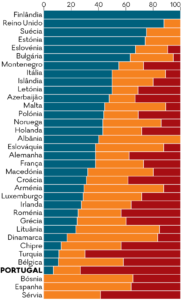 It is therefore not surprising that Portugal is the least compliant of 49 European countries in the fight against corruption. A report from the Council of Europe’s anti-corruption group (
It is therefore not surprising that Portugal is the least compliant of 49 European countries in the fight against corruption. A report from the Council of Europe’s anti-corruption group (