‘Look for the persons who benefit and you will know’ – Lenin
The four biggest economies in the Eurozone – Germany, France, Italy, and Spain – together represent two-thirds of the European Gross Domestic Product (GDP), an important indicator of economic health.
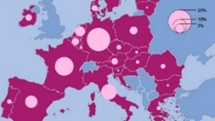
The Portuguese economy is relatively small – representing 1.5% of the European GDP – and surpassed by countries with less population like the Czech Republic, Sweden, Denmark, Austria, and Ireland.

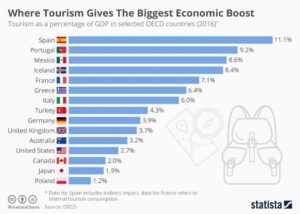
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts a growth in the Portuguese economy of 2.6% this year and stabilization at around 2% in the medium term, with a fall in inflation to 5.6%. Earlier this year, the IMF had predicted a growth of just 1%. The above-expected growth is mainly attributed to an increase in tourism – after the coronavirus pandemic – and the export of goods.

According to the Portuguese Government, export is increasing and represents 40% of its GDP. Cork is the most exported product – sold to 133 countries – reaching a record of 1.2 billion euros in 2021.
The quality newspaper Expresso disclosed that wine exportations last year – especially to the US, the UK, Canada, and Brazil – amounted to almost 1 billion euros. Portuguese wine is popular in every continent especially because of its original products like Green Wine, Port, and Madeira Wine.

Moreover, the country is the 4th biggest exporter of olive oil in the world and exports plenty of shoes, clothing, vegetables, and bicycles.

Last year a downward trend in debt and deficit was common in the Eurozone where public debt stood at 92% of GPD – four percentage points lower than at the end of 2021.Eurostat revealed that Portugal was able to register an even more pronounced reduction (eleven percentage points) in 2022, putting its actual public debt at 114%.
Even so, the Portuguese debt remains one of the highest of the 27 member states, just behind Greece and Italy.

The financial rating agency Fitch recently reaffirmed the assessment of the Portuguese debt at BBB+.
The robust reduction in public debt was also highlighted by the US agency, which forecasts that the Portuguese debt will further decrease to 105% next year.

Even though Portugal’s economy has grown above the EU average this year, it still has one of the lowest growth rates in the world.
According to the newspaper Expresso, the GDP in the country has grown at a mean rate of only 1.2% per year since 1999 and is unlikely to change its course by 2028.
Enjoy the week Aproveite a semana (pic Público/Sapo)






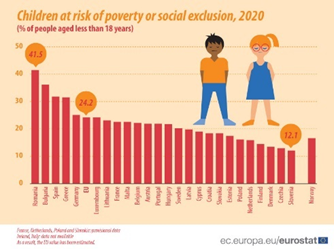

 The vast majority of the
The vast majority of the