
Before the pandemic, the Portuguese economy grew at a faster pace than the eurozone and the country ranked 28 on the list of wealthiest nations, despite its low rates in advanced education (50% of the population has only primary education; the highest percentage in Europe!) and average income (807 euro/month).
When the Chinese president Xi Jinping visited Portugal 18 months ago, the country willingly signed a multitude of cooperation agreements. At that time the socialist minority administration felt positive about the so-called ‘new Silk Route’.

In the meantime, its ‘golden visa program’ had opened the floodgates to Chinese buying up all sorts of property, banks, hotels and insurance companies.
But the tide has turned. The current public health crisis will drive a contraction in real GDP, and the long-lasting impact of the coronavirus on tourism will prevent a quick recovery in 2021.

An important economic lesson learnt, is to reduce dependence on imports from China. ‘This is the moment for Portugal to return to producing much of what we have been habitually importing’, Prime Minister António Costa declared.
To support the economy and prevent a debt crisis, Portugal can get 26.361 billion euros – 15.526 billion in grants and 10.835 billion in loans – from the European Economic Recovery Fund.

In order to access these funds, the country has to commit to the implementation of a reform plan program approved by the European Commission and the majority of the EU Council.
The government intends to use these assets to decarbonize the economy and reduce the imports of natural gas by developing an industry around hydrogen.
A European hub of ‘green energy’ (so-called because it is produced from renewable energy) close to Sines, one of the country’s major ports.

Sines is the perfect choice with its coal and oil-fired plants being disabled, and the network of existing gas pipelines 70% ready to distribute hydrogen. ‘Green hydrogen will be very cheap to produce and boost qualified employment’, says João Pedro MatosFernandes, the Minister for the Environment and Energetic transition

Another strategy to overcome the economic crisis caused by the pandemic, is to transform the country into ‘a cluster of industrialisation’, explains Minister of Foreign Affairs Augusto Santos Silva. ‘Portugal wants to be at Europe’s reindustrialisation forefront. We are talking here about textiles, clothing, shoes but also engineering, pharmaceuticals and agrifoods’.
He stressed that the country has important assets it can use like, qualified human resources, low wages, technology, quality of services and dominance in renewable energies.
Stay healthy Fique saudavel (pic Público/Sapo)

 There are roughly two ways to say tea in the world. One is like the English expression – thee in Dutch, tee in German or thé in French. The other is a variation of cha – chay in Russian, chai in Swahili or shay in Arabic. Both variations come from China. The words that sound like cha spread across the land, the tea saying spread over water.
There are roughly two ways to say tea in the world. One is like the English expression – thee in Dutch, tee in German or thé in French. The other is a variation of cha – chay in Russian, chai in Swahili or shay in Arabic. Both variations come from China. The words that sound like cha spread across the land, the tea saying spread over water.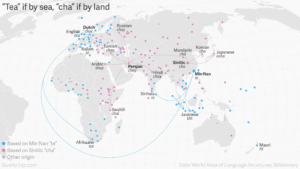 But the Chinese character for cha is pronounced as te in the Min Nan variety of Chinese, spoken in the coastal province of Fujian.
But the Chinese character for cha is pronounced as te in the Min Nan variety of Chinese, spoken in the coastal province of Fujian. Although it’s fairly commonly known that tea originated in China, it is far less known that it was a particular Portuguese woman, who inspired its popularity in England. Let’s go back to 1662, when
Although it’s fairly commonly known that tea originated in China, it is far less known that it was a particular Portuguese woman, who inspired its popularity in England. Let’s go back to 1662, when