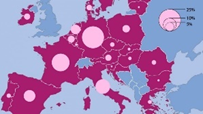
No stress, fresh food with fish and vegetables and a daily walk in nature

Bobi, the oldest dog in history, died last month on the 21st of October 2023, at the age of 31 years and 165 days.
He was awarded the title ‘oldest dog in the world’ by the Guinness Book of Records in February last year when he was 30 years old.

Bobi lived a quiet life in Conqueiros, a village in the municipality of Leiria, with the Costa family, eating mainly food for humans. He was lucky to have made it as the Costa children had to hide him for some time as the family had too many animals and the litter of four puppies was due to be euthanized.
The newborn dog was kept hidden for some time (hence his preference for human food), before becoming the longest-living pet in the Costa household.

He is described as a Rafeiro do Alentejo, a Portuguese guardian dog (named after its area of origin, the Alentejo province in southern Portugal). Dogs of this type were traditionally kept to protect flocks. In 1954 the breed was officially acknowledged by the Fédération Cynologique Internationale.

His 31st birthday was a relatively busy affair with about 100 guests coming from all over the world wanting to take pictures of him. Even so, he managed to eat his favorite dish of grilled pork and fish, enjoyed a folklore dance put in his honor, and took several naps during the day.

Veterinarian Peter Dobias flew in from Canada with his dog Pats for the event which he described as inspiring. ‘We would all love our dogs to live long. They say if you don’t have friends you have a 50% chance of encountering more health problems. Bobi has friends and an amazing family teaching me how to take care of my dog.’

Other veterinarians present at the birthday party in Leiria declared that the secret of the dog’s longevity must lie in a calm life without stress, a rich social life, non-processed fresh and diverse human food with everyday fish and vegetables from the organic garden, and daily nature walks with his owner Lionel, who got Bobi when he was 8 years old.
Guinness World Records are looking into claims after skepticism over whether the Portuguese mastiff really lived over 31 years.

Danny Chambers, a vet and member of the Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons said: ‘this is the equivalent of a human living over 200 years, which is completely implausible’ adding that Bobi’s example had been taken up by anti-pet food zealots ‘who are campaigning that dog food is killing pets’.
Enjoy the week Aproveite a semana (pic Público/Ptresid)